Modular vs. Monolithic Blockchain Comparison Tool
Splits core functions into separate, specialized layers for enhanced scalability, security, and flexibility.
- Separate consensus, execution, data availability, settlement
- High throughput (1,000-10,000+ TPS)
- Independent upgrades without full network forks
- Built-in interoperability with cross-chain protocols
Bundles all functions into a single codebase, limiting scalability and upgrade options.
- Single integrated architecture
- Limited throughput (10-100 TPS)
- Network-wide hard forks for upgrades
- Isolated systems requiring external bridges
| Dimension | Modular | Monolithic |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability (TPS) | 1,000-10,000+ | 10-100 |
| Upgrade Flexibility | Layer-specific upgrades, no full chain fork | Network-wide hard forks required |
| Cost per Tx | Low - parallel processing reduces gas | Higher - limited block space |
| Complexity | Higher - multi-layer architecture | Lower - single codebase |
| Interoperability | Built-in cross-chain protocols (IBC, bridges) | Often isolated, need external bridges |
Select your requirements to determine which blockchain architecture suits your project best:
Recommended Architecture:
Quick Takeaways
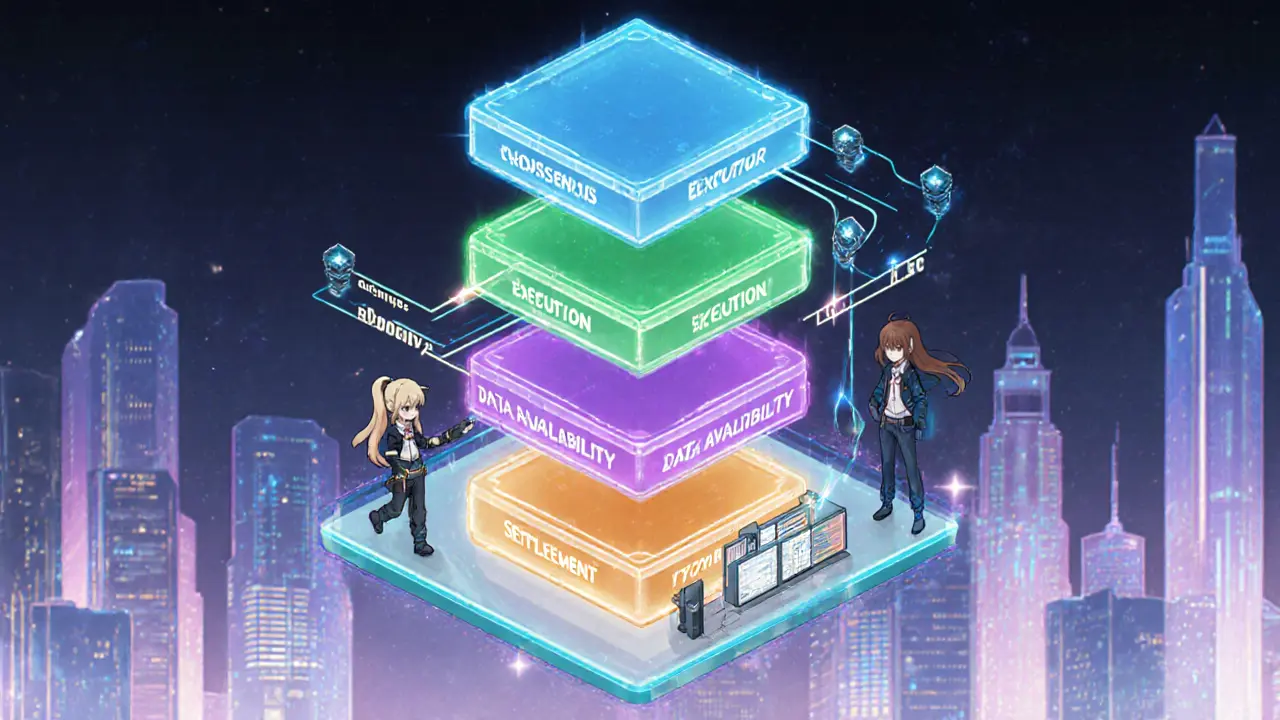
- Layered architecture separates consensus, execution, data availability, and settlement, letting each part be optimized.
- Scalability jumps from dozens to thousands of TPS because work happens in parallel.
- Security improves as each layer can be hardened independently without breaking the whole system.
- Developers gain flexibility - they can pick the execution engine or data‑availability solution that best fits their app.
- Real‑world projects like Polygon, Polkadot and Cosmos already prove the model works at scale.
When you hear the term modular blockchain is an architectural style that splits core blockchain functions into separate, specialist layers, the first question is usually “why bother?”. The answer boils down to three classic pain points of early blockchains - limited throughput, rigid upgrades and costly resource use. By unbundling consensus, execution, data availability and settlement, a modular setup lets each piece evolve on its own, delivering the sweet spot of the blockchain trilemma: high security, strong decentralization and real‑world scalability.
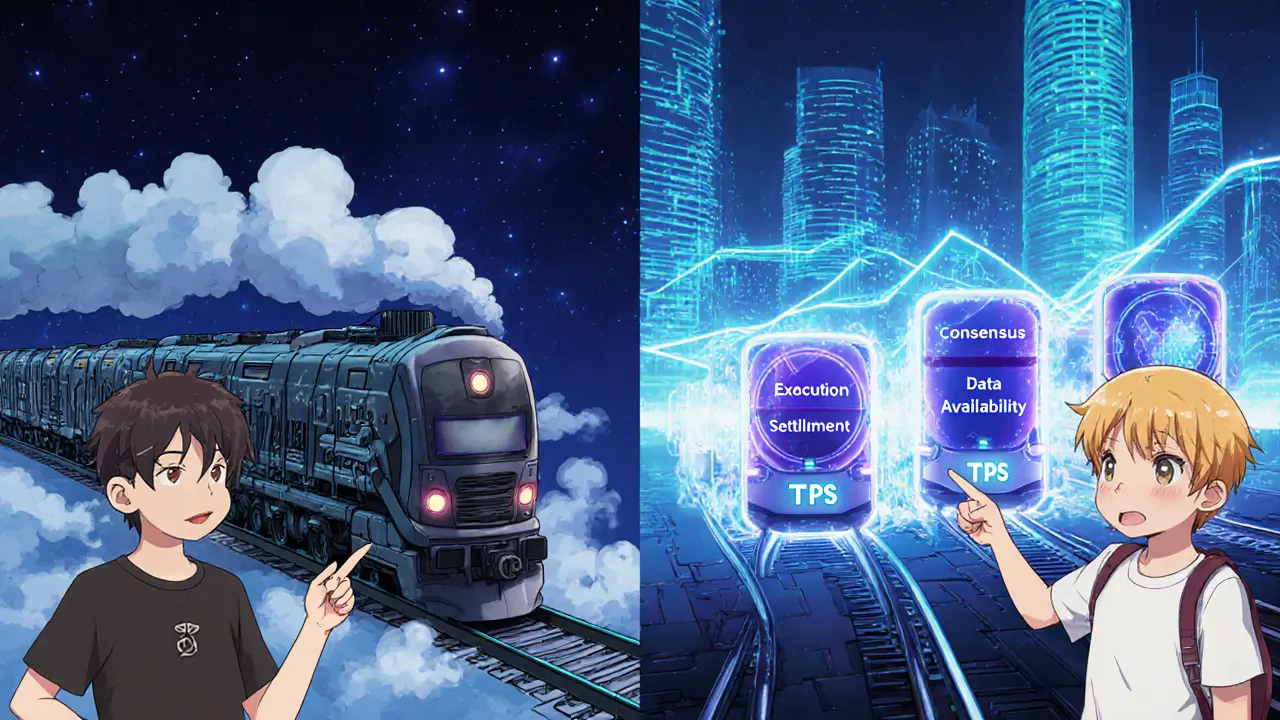
What Exactly Is a Modular Blockchain?
Think of a traditional monolithic chain as a single‑track train: every carriage - consensus, transaction execution, state storage - rides on the same rail and must move at the speed of the slowest part. A modular blockchain, on the other hand, builds a multi‑track system where each function gets its own dedicated rail.
Key layers include:
- Consensus layer defines how nodes agree on new blocks - e.g., proof‑of‑stake, BFT.
- Execution layer runs smart‑contract code and updates state - often a virtual machine like EVM or WASM.
- Data availability layer stores block data and serves it to validators - can be a separate roll‑up or data‑availability committee.
- Settlement layer finalizes transactions and provides finality guarantees - often a slower, ultra‑secure chain.
Because each layer talks through well‑defined protocols, you can swap a faster execution engine without touching consensus, or add a new data‑availability solution without rebooting the whole network.
Scalability - The Most Visible Win
Parallel processing is the secret sauce. In a monolithic chain, a validator must execute every transaction sequentially before it can seal the block. With modular design, the execution layer can process thousands of transactions in parallel while the consensus layer only needs to agree on a succinct proof that the work was done correctly. Real‑world numbers back this up: Polygon’s roll‑up architecture routinely hits 7,000TPS, and Cosmos zones report several thousand TPS across interoperable chains.
Higher throughput translates directly into lower fees. When block space is abundant, users stop battling sky‑high gas prices, and developers can design richer dApps without worrying about cost‑driven bottlenecks.
Security Benefits Without Sacrificing Speed
Each layer can be audited and hardened on its own. The consensus layer can stick with a battle‑tested BFT algorithm, while the execution layer experiments with a new virtual machine. If a bug shows up in the VM, you can patch or replace it without re‑engineering the entire consensus mechanism. This compartmentalization reduces the blast radius of exploits and makes formal verification more tractable.
Moreover, the settlement layer often runs on a highly secure, low‑throughput chain (think Cosmos Hub or Ethereum mainnet) that provides finality. Even if an execution or data‑availability layer is compromised, the settlement layer can reject invalid proofs, preserving overall network integrity.
Flexibility and Interoperability - Building a Multi‑Chain Ecosystem
Developers love the ability to choose the best tool for the job. Need a high‑speed EVM‑compatible environment? Plug in an execution layer that runs the Optimism roll‑up. Want to run Rust‑based smart contracts? Swap in a WASM execution layer. The data‑availability layer can be a separate Celestia network or a custom availability committee, depending on regulatory or performance needs.
Interoperability is baked in. Protocols like IBC (Inter‑Blockchain Communication) connect Cosmos zones, while Polkadot’s parachain model lets many independent chains share a common relay chain for settlement. This cross‑chain communication reduces silo‑effect and opens the door to complex DeFi compositions across networks.
Real‑World Implementations
Three projects illustrate how modular design works in practice:
- Polygon a multi‑layer scaling solution for Ethereum that separates roll‑up execution from Ethereum’s base layer - delivers high TPS and low fees while relying on Ethereum for settlement.
- Polkadot a relay‑chain based ecosystem where parachains handle execution and consensus independently - enables heterogeneous blockchains to share security.
- Cosmos an ecosystem of independent zones linked by the IBC protocol and a shared hub for settlement - champions modularity and interoperability.
All three have launched mainnets, attracted developer ecosystems, and processed billions of dollars in transaction volume, proving that modularity isn’t just theory.
Challenges to Keep in Mind
Modular designs bring complexity. Teams must understand how layers communicate, manage cross‑layer latency, and secure multiple attack surfaces. The learning curve can be steep for developers accustomed to a single‑chain workflow.
Documentation quality varies. While Polygon and Polkadot have extensive guides, newer data‑availability solutions like Celestia are still maturing. Organizations should budget extra time for architecture design and testing.
Finally, because many modular networks are younger than Bitcoin or Ethereum, they have less battle‑testing under extreme load. Risk‑averse businesses may want to start with a well‑audited execution layer on a proven settlement chain before fully committing.
Getting Started - A Practical Checklist
- Define your performance goals: TPS, latency, cost per transaction.
- Select a settlement layer that meets your security and finality requirements (e.g., Ethereum, Cosmos Hub).
- Choose an execution layer that supports your smart‑contract language (EVM, WASM, etc.).
- Pick a data‑availability solution that aligns with your throughput needs and regulatory stance.
- Set up inter‑layer communication protocols (IBC, cross‑chain messaging, etc.).
- Run security audits on each layer independently before integrating.
- Deploy a testnet that mimics the full stack to uncover latency or compatibility bugs.
- Iterate - once the layers are stable, you can upgrade or replace individual components without a full network halt.
Following this checklist reduces the initial overwhelm and lets you reap modular benefits faster.
Future Outlook - Why Modular Might Dominate New Projects
Analysts predict that most new blockchain protocols launched after 2025 will adopt a layered architecture from day one. The pressure to handle enterprise‑scale applications, coupled with the need for regulatory flexibility, makes modularity a natural fit. Upcoming improvements in cross‑layer messaging (e.g., faster proofs, lower latency) aim to tame the current complexity barrier.
In the long run, we may see a “layer marketplace” where developers can rent specialized execution or data‑availability services on demand, much like cloud infrastructure today. That would further accelerate innovation, allowing anyone to spin up a custom blockchain with just a few clicks.
| Dimension | Modular | Monolithic |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability (TPS) | 1,000‑10,000+ | 10‑100 |
| Upgrade Flexibility | Layer‑specific upgrades, no full chain fork | Network‑wide hard forks required |
| Cost per Tx | Low - parallel processing reduces gas | Higher - limited block space |
| Complexity | Higher - multi‑layer architecture | Lower - single codebase |
| Interoperability | Built‑in cross‑chain protocols (IBC, bridges) | Often isolated, need external bridges |

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between modular and monolithic blockchains?
Modular blockchains split core functions (consensus, execution, data availability, settlement) into separate layers that can be optimized and upgraded independently, while monolithic chains bundle everything into one codebase, limiting parallelism and upgrade flexibility.
Can I use a modular blockchain with existing Ethereum smart contracts?
Yes. Many modular solutions (e.g., Polygon, Optimism) run an EVM‑compatible execution layer that accepts standard Solidity contracts, while delegating consensus and settlement to Ethereum’s base chain.
Is a modular architecture more secure than a monolithic one?
Security improves because each layer can be hardened separately and the settlement layer provides finality. However, overall security depends on the implementation quality of all layers; more components can mean more attack surfaces if not properly audited.
What are the biggest challenges when building on a modular blockchain?
The steep learning curve, need for expertise in multiple layers, managing cross‑layer latency, and ensuring consistent security across components are the main hurdles. Documentation gaps in newer layers can also slow development.
Will modular blockchains replace monolithic ones entirely?
Not likely in the short term. Monolithic chains still dominate for simple use‑cases and have massive battle‑tested security. Modular designs will grow where high throughput, customizability, and cross‑chain interaction are critical.

Mark Camden
October 27, 2024 AT 03:17When discussing blockchain architecture, one must recognize the moral responsibility to pursue systems that do not sacrifice user security for mere novelty. The modular approach offers a principled path that aligns with the broader ethical mandate of decentralization.
Prince Chaudhary
November 6, 2024 AT 03:17The modular design really opens doors for developers eager to experiment without breaking the whole chain. It’s energizing to see such flexibility in action.
John Kinh
November 16, 2024 AT 03:17Sure, modular sounds cool 😒 but the hype often outpaces the real‑world performance.
Evie View
November 26, 2024 AT 03:17Modular hype fuels unrealistic expectations and blinds people to the risks. The excitement can become a dangerous distraction.
Sidharth Praveen
December 6, 2024 AT 03:17Seeing the scalability gains from separating layers is truly uplifting. Keep pushing forward, the ecosystem thrives on optimism.
Sophie Sturdevant
December 16, 2024 AT 03:17From a technical coaching standpoint, modularity introduces a stack of interchangeable modules-consensus, execution, data availability-each with its own SLA. This granularity empowers teams to benchmark and iterate with precision, accelerating time‑to‑market while maintaining compliance.
Nathan Blades
December 26, 2024 AT 03:17Modular blockchains are reshaping the scalability narrative by literally separating concerns.
When you detach consensus from execution, you free the CPU to crunch transactions in parallel.
That parallelism translates into thousands of TPS without sacrificing the security guarantees of the underlying settlement layer.
Developers can cherry‑pick an execution environment that matches their language preferences, whether that's EVM, WASM, or something experimental.
Because each layer communicates through well‑defined proof protocols, upgrades become surgical rather than systemic.
A single layer can be upgraded without forcing the entire network into a hard fork, reducing governance friction.
Security benefits arise from this compartmentalization, as a bug in the data‑availability module does not automatically compromise consensus.
Conversely, the settlement layer can remain a conservative, battle‑tested chain, providing finality that other layers inherit.
Interoperability also blooms, since standardized cross‑layer messaging enables seamless asset transfers across otherwise isolated ecosystems.
Projects like Cosmos, Polkadot, and Polygon have already demonstrated these principles at scale.
Their real‑world throughput numbers back the theory, often reaching the high‑single‑digit‑thousands per second.
Nevertheless, the added architectural complexity demands rigorous testing and a deeper expertise from dev teams.
Cross‑layer latency can become a bottleneck if the proof verification is not optimized.
But with advances in succinct cryptography, those delays are shrinking rapidly.
In summary, modular design offers a pragmatic path to the blockchain trilemma, balancing speed, security, and decentralization for the next generation of dApps.
Somesh Nikam
January 5, 2025 AT 03:17The layered approach gives developers a clear roadmap for incremental upgrades 😊. It also simplifies debugging because each component can be isolated and tested thoroughly.
Jan B.
January 15, 2025 AT 03:17Modular is the future.
MARLIN RIVERA
January 25, 2025 AT 03:17The so‑called ‘modular advantage’ is merely a marketing veneer that masks underlying fragility. Without a unified security model the system becomes a patchwork of weak links.
Debby Haime
February 4, 2025 AT 03:17Don’t let the complexity intimidate you; every new layer is an opportunity to innovate faster. Ride the wave of modularity and watch your projects take off.
emmanuel omari
February 14, 2025 AT 03:17From an engineering perspective, modular architecture reduces the probability of catastrophic failure by isolating fault domains. Each layer can be audited independently, which streamlines compliance across jurisdictions.
Andy Cox
February 24, 2025 AT 03:17It's interesting to see how the community adopts these designs at a relaxed pace, allowing culture to shape technical standards.
Courtney Winq-Microblading
March 6, 2025 AT 03:17Think of modular blockchains as a philosophical tapestry, each thread representing a distinct function yet woven into a cohesive whole. When the consensus layer hums in harmony with execution, the system breathes a kind of digital serenity that transcends mere transaction throughput. Moreover, the interplay of layers invites a reflective dialogue about the nature of trust and decentralization. It’s not just engineering-it’s an artistic statement on how we choose to distribute power across a network.
katie littlewood
March 16, 2025 AT 03:17Honestly, the modular narrative feels like the perfect blend of ambition and practicality; on one hand, you get this exhilarating promise of unlimited scalability, and on the other, you retain the comforting familiarity of established security models. The brilliance lies in the fact that developers can now pick and choose execution engines like a gourmet chef selecting spices-EVM for the classic palate, WASM for the avant‑garde, or even emerging runtimes for experimental flavors. This modularity doesn’t merely boost TPS numbers; it democratizes innovation, allowing small teams to iterate on isolated layers without the bureaucratic nightmare of a monolithic overhaul. Of course, there’s a learning curve-multiple SDKs, cross‑layer messaging, and proof verification can feel like juggling flaming torches-but the payoff is a resilient, adaptable ecosystem that can pivot as market demands evolve. In short, modular blockchains are the Swiss army knife of the crypto world, offering versatility, precision, and a touch of elegance that monolithic designs simply can’t match.
Jenae Lawler
March 26, 2025 AT 03:17While proponents herald modularity as a panacea, it inevitably introduces an additional attack surface that sophisticated adversaries will inevitably exploit; the trade‑off between flexibility and security is far from trivial.
Chad Fraser
April 5, 2025 AT 04:17Let’s keep the conversation inclusive-anyone can build on a modular stack regardless of prior experience. The community thrives when we mentor newcomers and share best practices.
Jayne McCann
April 15, 2025 AT 04:17Modular hype is overrated; simplicity often outperforms complexity.